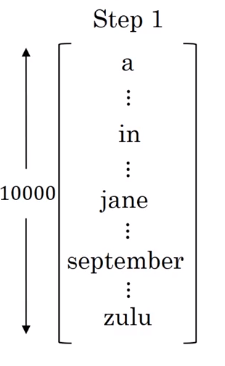

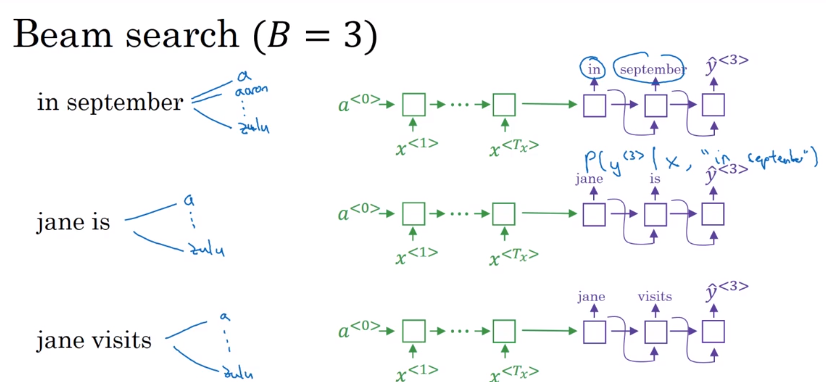
B which is the beam width. Lets take B = 3 which means the algorithm will get 3 outputs at a time.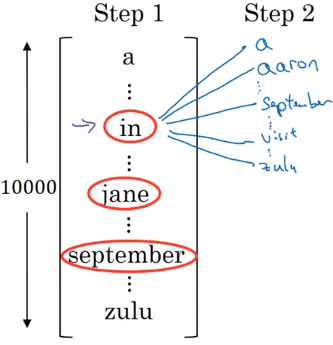
We will have then [“in september”, “jane is”, “jane visit”]. These three words are kept in the memory.
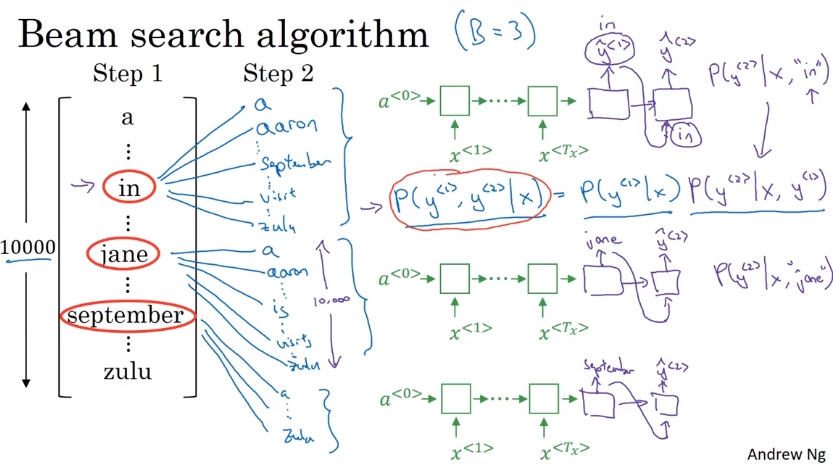 Notice, that we automatically discard september as a first word.
Notice, that we automatically discard september as a first word.
B = 1 this will become the greedy search.
arg
arg
In practice, slightly softer approach may be taken with addition of where is around 0.7 in practice.
The second thing is how can we choose best B?
Unlike exact search alrogithms like BFS or DFS, Beam Search runs faster but is not guaranteed to find exact maximum for arg
See here
# coding: utf-8 """ Beam search for neural network sequence to sequence (encoder-decoder) models. Usage example: from beam_search import beam_search # Load model and vocabularies... input_text = "Hello World !" X = [encoder_vocabulary.get(t, encoder_vocabulary['<UNK>']) for t in input_text.split()] hypotheses = beam_search(model.initial_state_function, model.generate_function, X, decoder_vocabulary['<S>'], decoder_vocabulary['</S>']) for hypothesis in hypotheses: generated_indices = hypothesis.to_sequence_of_values() generated_tokens = [reverse_decoder_vocabulary[i] for i in generated_indices] print(" ".join(generated_tokens)) """ import numpy as np class Node(object): def __init__(self, parent, state, value, cost, extras): super(Node, self).__init__() self.value = value self.parent = parent # parent Node, None for root self.state = state.flatten() if state is not None else None # recurrent layer hidden state self.cum_cost = parent.cum_cost + cost if parent else cost # e.g. -log(p) of sequence up to current node (including) self.length = 1 if parent is None else parent.length + 1 self.extras = extras # can hold, for example, attention weights self._sequence = None def to_sequence(self): # Return sequence of nodes from root to current node. if not self._sequence: self._sequence = [] current_node = self while current_node: self._sequence.insert(0, current_node) current_node = current_node.parent return self._sequence def to_sequence_of_values(self): return [s.value for s in self.to_sequence()] def to_sequence_of_extras(self): return [s.extras for s in self.to_sequence()] def beam_search(initial_state_function, generate_function, X, start_id, end_id, beam_width=4, num_hypotheses=1, max_length=50): """Beam search for neural network sequence to sequence (encoder-decoder) models. :param initial_state_function: A function that takes X as input and returns state (2-dimensonal numpy array with 1 row representing decoder recurrent layer state - currently supports only one recurrent layer). :param generate_function: A function that takes X, Y_tm1 (1-dimensional numpy array of token indices in decoder vocabulary generated at previous step) and state_tm1 (2-dimensonal numpy array of previous step decoder recurrent layer states) as input and returns state_t (2-dimensonal numpy array of current step decoder recurrent layer states), p_t (2-dimensonal numpy array of decoder softmax outputs) and optional extras (e.g. attention weights at current step). :param X: List of input token indices in encoder vocabulary. :param start_id: Index of <start sequence> token in decoder vocabulary. :param end_id: Index of <end sequence> token in decoder vocabulary. :param beam_width: Beam size. Default 4. :param num_hypotheses: Number of hypotheses to generate. Default 1. :param max_length: Length limit for generated sequence. Default 50. """ if isinstance(X, list) or X.ndim == 1: X = np.array([X], dtype=np.int32).T assert X.ndim == 2 and X.shape[1] == 1, "X should be a column array with shape (input-sequence-length, 1)" next_fringe = [Node(parent=None, state=initial_state_function(X), value=start_id, cost=0.0, extras=None)] hypotheses = [] for _ in range(max_length): fringe = [] for n in next_fringe: if n.value == end_id: hypotheses.append(n) else: fringe.append(n) if not fringe or len(hypotheses) >= num_hypotheses: break Y_tm1 = np.array([n.value for n in fringe], dtype=np.int32) state_tm1 = np.array([n.state for n in fringe], dtype=np.float32) state_t, p_t, extras_t = generate_function(X, Y_tm1, state_tm1) Y_t = np.argsort(p_t, axis=1)[:,-beam_width:] # no point in taking more than fits in the beam next_fringe = [] for Y_t_n, p_t_n, extras_t_n, state_t_n, n in zip(Y_t, p_t, extras_t, state_t, fringe): Y_nll_t_n = -np.log(p_t_n[Y_t_n]) for y_t_n, y_nll_t_n in zip(Y_t_n, Y_nll_t_n): n_new = Node(parent=n, state=state_t_n, value=y_t_n, cost=y_nll_t_n, extras=extras_t_n) next_fringe.append(n_new) next_fringe = sorted(next_fringe, key=lambda n: n.cum_cost)[:beam_width] # may move this into loop to save memory hypotheses.sort(key=lambda n: n.cum_cost) return hypotheses[:num_hypotheses]
Usage example:
from beam_search import beam_search # Load model and vocabularies... input_text = "Hello World !" X = [encoder_vocabulary.get(t, encoder_vocabulary['<UNK>']) for t in input_text.split()] hypotheses = beam_search(model.initial_state_function, model.generate_function, X, decoder_vocabulary['<S>'], decoder_vocabulary['</S>']) for hypothesis in hypotheses: generated_indices = hypothesis.to_sequence_of_values() generated_tokens = [reverse_decoder_vocabulary[i] for i in generated_indices] print(" ".join(generated_tokens))`