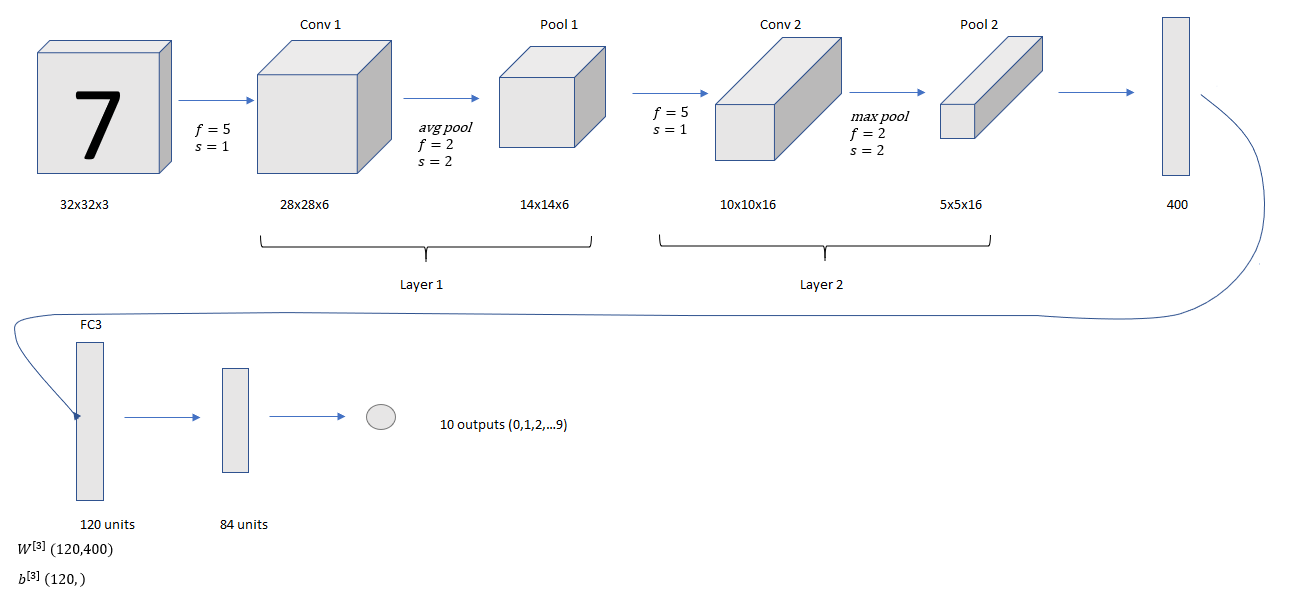

In modern implementation, avg pool is replaced by max pool and sigmoid/tanh was replaced by softmax with 10 class output.
conv pool conv pool FC FC output structure is still common.Implementation of LeNet 5 in Keras
# Implementation of LeNet-5 in keras # [LeCun et al., 1998. Gradient based learning applied to document recognition] # Some minor changes are made to the architecture like using ReLU activation instead of # sigmoid/tanh, max pooling instead of avg pooling and softmax output layer import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd train = pd.read_csv('train.csv') test = pd.read_csv('test.csv') Y_train = train[['label']] X_train = train.drop(train.columns[[0]], axis=1) X_test = test #Visualizing the data sample = X_train.iloc[10, :] sample = sample.reshape([28,28]) plt.imshow(sample, cmap='gray') X_train = np.array(X_train) X_test = np.array(X_test) #Reshape the training and test set X_train = X_train.reshape(X_train.shape[0], 28, 28, 1) X_test = X_test.reshape(X_test.shape[0], 28, 28, 1) #Padding the images by 2 pixels since in the paper input images were 32x32 X_train = np.pad(X_train, ((0,0),(2,2),(2,2),(0,0)), 'constant') X_test = np.pad(X_test, ((0,0),(2,2),(2,2),(0,0)), 'constant') #Standardization mean_px = X_train.mean().astype(np.float32) std_px = X_train.std().astype(np.float32) X_train = (X_train - mean_px)/(std_px) #One-hot encoding the labels from keras.utils.np_utils import to_categorical Y_train = to_categorical(Y_train) import keras from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Conv2D from keras.layers import MaxPooling2D from keras.layers import Flatten from keras.layers import Dense model = Sequential() #Layer 1 #Conv Layer 1 model.add(Conv2D(filters = 6, kernel_size = 5, strides = 1, activation = 'relu', input_shape = (32,32,1))) #Pooling layer 1 model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size = 2, strides = 2)) #Layer 2 #Conv Layer 2 model.add(Conv2D(filters = 16, kernel_size = 5, strides = 1, activation = 'relu', input_shape = (14,14,6))) #Pooling Layer 2 model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size = 2, strides = 2)) #Flatten model.add(Flatten()) #Layer 3 #Fully connected layer 1 model.add(Dense(units = 120, activation = 'relu')) #Layer 4 #Fully connected layer 2 model.add(Dense(units = 84, activation = 'relu')) #Layer 5 #Output Layer model.add(Dense(units = 10, activation = 'softmax')) model.compile(optimizer = 'adam', loss = 'categorical_crossentropy', metrics = ['accuracy']) model.fit(X_train ,Y_train, steps_per_epoch = 10, epochs = 42) y_pred = model.predict(X_test) #Converting one hot vectors to labels labels = np.argmax(y_pred, axis = 1) index = np.arange(1, 28001) labels = labels.reshape([len(labels),1]) index = index.reshape([len(index), 1]) final = np.concatenate([index, labels], axis = 1) #Prediction csv file np.savetxt("mnist_1.csv", final, delimiter = " ", fmt = '%s')
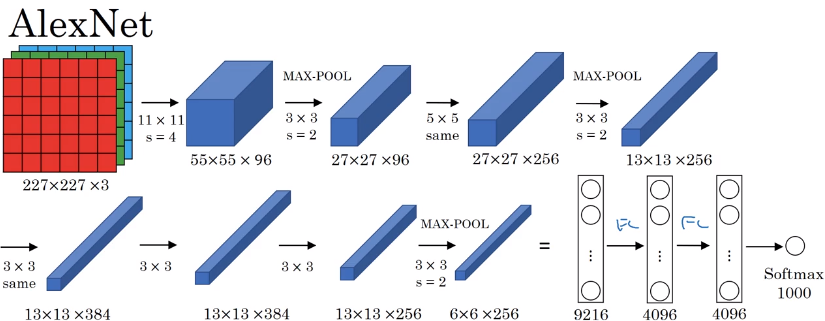
Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey E. Hinton. 2012. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems - Volume 1 (NIPS’12), F. Pereira, C. J. C. Burges, L. Bottou, and K. Q. Weinberger (Eds.), Vol. 1. Curran Associates Inc., USA, 1097-1105.
A remarkable thing about the VGG-16 net is that instead of having so many hyperparameters, it use a much simpler network where just having a conv-layers that are just three-by-three filters with a stride of one and always use same padding. Conv=3x3 filter, s=1, same Padding Max pool = 2x2, s=2
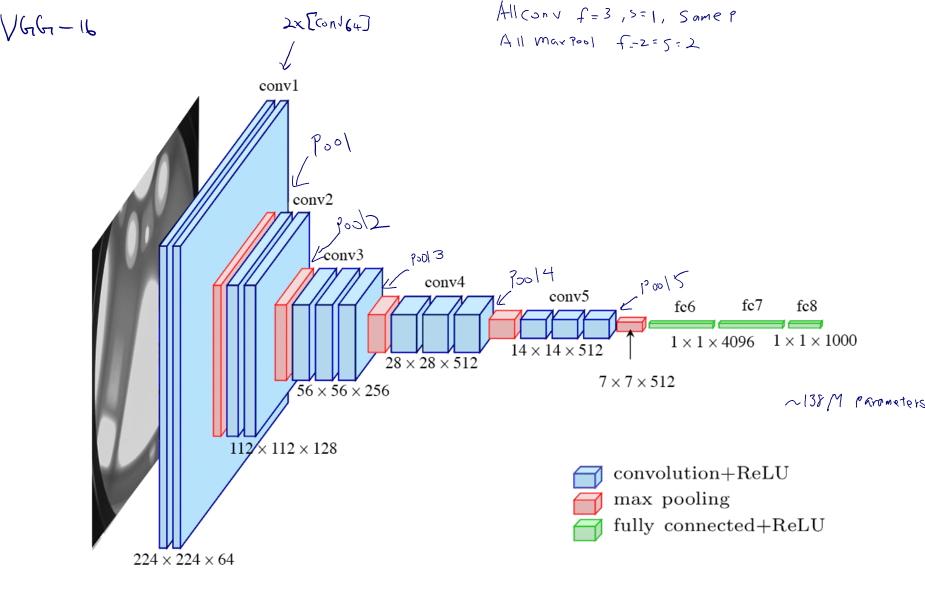
VGG -19 is used in some literature, but VGG -16 works as good as VGG -19.
LeCun et al., 1998: Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition (Proc. IEEE 1998)
Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey E. Hinton. 2012. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems - Volume 1 (NIPS’12), F. Pereira, C. J. C. Burges, L. Bottou, and K. Q. Weinberger (Eds.), Vol. 1. Curran Associates Inc., USA, 1097-1105.
K. Simonyan, A. Zisserman, Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition, ICLR 2015 https://youtu.be/OQe-9P51Z0s