Exponentially weighted averages
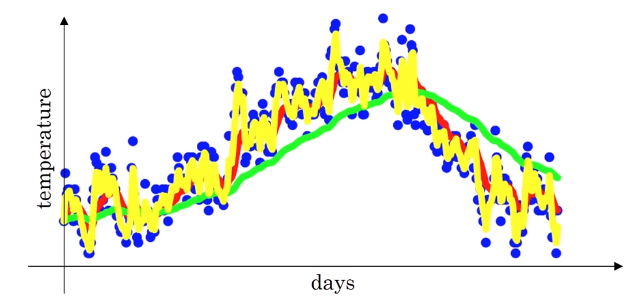
Daily temperature in London
To compute the trends, the local average or a moving average of the temperature, here is the steps:
1.Initialize
gives which is exponentially weighted average
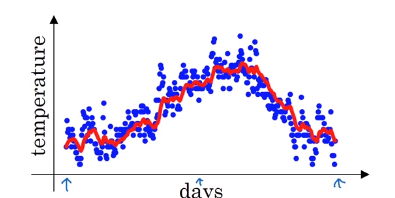
Exponentially weighted averages
average over day’s temperature, so
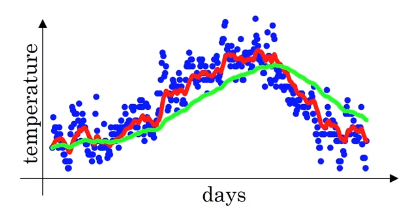
- 10 days’s average temperature
- 50 days’s average temperature
Notice:
- The higher gives more smoother curve because it is the average of more days
- The higher gives slower adaptation of new temperature (more latency) since the weight to the current temperature is very small.
- 2 days’s average temperature
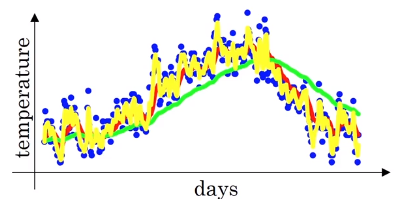
Notice:
- More noisy
- More susceptible to outliers
- Quicker to adapt to a new temperature
Understanding of exponentially weighted averages
Exponentially weighted averages will turn out to be a key component of several optimization algorithms that you used to train your neural networks.
gives following:
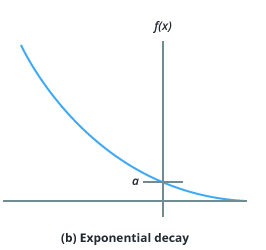
Let’s and write few equations:
So,
☝️ Exponentially decaying function
Implementation of exponentially weighted averages
How do you implement below?
In practice:
Repeat {
get next
}






